citizen reporting
Posted by KatrinVerclas on Aug 14, 2007
We are pleased to welcome Bart Lacroix to MobileActive.org. He will be writing an occasional blog on AfricaNews' Voices of Africa project, an experiment in mobile citizen reporting. AfricaNews currently has three citizen reporters covering stories in their using mobile countries, phones to produce video footage, written reports and photographs.
Using GPRS-enabled phones, on-the-ground citizens reporters don’t need an internet connection at all - only mobile coverage - to send video, voice, and text. The Voices of Africa is deploying reporters in Ghana, South Africa, and Kenya to date who are using Nokia E61i phones to send in their stories. These countries have, admittedly, better mobile coverage than others, so are good for this pilot project. Bart will tell us how it's going, what citizens are reporting on, and what they are learning about content and technical production before sacaling up the project.
A bit of background from AfricaNews' press release:
Posted by AnneryanHeatwole on Jun 27, 2011
Have you ever had a problem with your neighborhood and wanted to rally your community around finding a solution? Commons, a mobile mapping and reporting game, does just that. Commons is an iPhone app that allows players to locate their position on a map and then guides the players through a series of challenges to report and comment on their neighborhood. Reports can be voted on, so users who submit the best reports or images can win badges that show their involvement. The first real-world gameplay happened lower Manhattan in New York City on June 19th at the Come Out and Play Festival.
| Commons: Real-World Games for Change data sheet 6081 Views |
| Countries: |
United States
|
Posted by MohiniBhavsar on Jun 29, 2010
Networked Activism data sheet 1806 Views
Abstract:
The same technologies that groups of ordinary citizens are using to write operating systems and encyclopedias are fostering a quiet revolution in another area - social activism. On websites such as Avaaz.org and Wikipedia, citizens are forming groups to report on human rights violations and organize email writing campaigns, activities formerly the prerogative of professionals. This article considers whether the participatory potential of technology can be used to mobilize ordinary citizens in the work of human rights advocacy.
Existing online advocacy efforts reveal a de facto inverse relationship between broad mobilization and deep participation. Large groups mobilize many individuals, but each of those individuals has only a limited ability to participate in decisions about the group’s goals or methods. Thus, although we currently have the tools necessary for individuals to engage in advocacy without the need for professional organizations, we are still far from realizing an ideal of fully decentralized, user-generated activism.
Drawing on the insights of network theory, the article proposes a model of “networked activism” that would help ensure both deep participation and broad mobilization by encouraging the formation of highly participatory small groups while providing opportunities for those small groups to connect with one another. Drawing on a series of interviews with human rights and other civil society organizations, the article recommends specific design elements that might foster a model of networked activism. The article concludes that although online activism is unlikely to replace some of the functions served by human rights organizations, efforts to create synergies between traditional and online efforts have the potential to provide avenues for real, meaningful, and effective citizen participation in human rights advocacy.
Posted by MelissaUlbricht on Jun 21, 2010
We are very interested in the role of mobile phones in citizen media, including how mobile phones can function as a portable newsroom or radio studio. To that end, our latest how-to guide, Mobile Audio Recording in the Field (and how to get a clear sound on the streets), walks you through the process of recording audio content on your mobile phone, whether you are recording from a studio, your home, or in the field.
This how-to is part of the Mobile Media Toolkit, which includes many other case studies, how-to guides, resources, and tools to use mobile phones for reporting, content delivery, and citizen participation.
The how-to provides:
Posted by admin on May 31, 2010
Recently, we’ve been seeing a lot of hype about citizen reporting with mobile phones during elections. It is often conflated with the term “election monitoring,” but this does a disservice to both citizen reporting and election monitoring, a discipline and field that has been around for some 20 years. These two approaches have markedly different goals, target audiences, and processes. We think it is time for readers to definitively understand what election monitoring is in contrast to citizen reporting, and what the role of mobile phone and mapping platforms are in regard to these two very different forms of engagement during elections. We aim to clearly differentiate between them once and for all.
We also urge the adoption of differing terms - citizen reporting during an election versus systematic election monitoring. Mobile phones, SMS, and mapping platforms play a role in both citizen reporting and election monitoring, of course.
Posted by AnneryanHeatwole on Feb 08, 2010
The National Democratic Institute and MobileActive.org are hosting "New Tools for Better Elections", a conference on February 26th on new technologies for fair, representative and equitable elections. In preparation for the event, we sat down with Ian Schuler, Senior Manager of Information and Communications Technology Programs at the National Democratic Institute. Schuler specializes in the application of mobile technology for the advancement of democracy and human rights, He is the author of SMS as a Tool in Election Observation.
In this conversation, Schuler breaks down not only the differences between election observation, citizen reporting, and crowd-sourcing, but also explains why these distinctions matter and how mobile technology is changing the way elections are held. Read on for excerpts from our conversation, or scroll down to watch the interview in its entirety.
Q: You and NDI have done a lot of election monitoring around the world. Explain why election monitoring matters.
A: Elections are the main process by which people participate in their government by selecting their leaders. People expect that it’s going to be a fair process, and that it’s going to be an accurate process. So it’s important for people to have confidence to know that somebody is really systematically watching the entire process to make sure that it is good. Election monitoring prevents fraud by making it harder for the people who want to manipulate elections to do so; it detects fraud when it happens, and it lets people know if the process was good – and if it was not, what were the problems and what might be constructive, non-violent ways of remedying those problems, whether it’s simply improving the process for later or rerunning elections or whatever is warranted in that situation.
Posted by KatrinVerclas on Dec 31, 2008
Some people are claiming that the conflict in Gaza is a "social war." But so far, social media is used mainly for propaganda and there is a marked absence of voices from people affected by the conflict, and of useful applications of mobile and other social media. As the Israeli bombing of Gaza is continuing and is now in its third day, mobile communication is beginning to make the news but is not playing the dominant role in citizen reporting and aid communications as it has in other conflicts.
A few examples that have not been reported anywhere else: Souktel, an organization in Ramallah that is known for its SMS-job matching service connecting Palestine youth with work, is running a Palestinian "SMS Blood Bank" program for the Red Crescent.
Posted by CorinneRamey on Jan 21, 2008
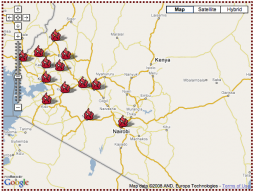
Post-election violence has exploded in Kenya in the wake of the December 27 presidential elections. Ethnic killings -- which today's New York Times suggests may have been carefully planned -- have increased, and estimates of the death toll range from 650 to over 1000. In the midst of this, people both in and outside the country are using mobile phones in innovative ways to communicate political knowledge and circumvent the media blackout.
Posted by bartlacroix on Aug 16, 2007
Mobile phones change the media landscape in Africa. AfricaNews (www.africanews.com) starts working with mobile phone reporters. The mobile reporters cover current events in their area, using the mobile phones to produce video footage, written reports and photographs. With this innovative project, African citizens – from the sprawling metropolises to the most isolated villages – can let their voices be heard across the continent and around the world.
Africa is witnessing impressive growth in the development and use of mobile communication networks and the Internet. This development is changing the face of media and the way people are informed. Open communication and uncensored exchange of opinions are helping to build transparent societies. This serves good governance and helps to build stronger democracies.